To achieve the net-zero energy goals energy efficiency was considered for all stages of the lifecycle of the building. Several configurations for envelope materials and technologies were evaluated using a building energy model. The selected configurations were the result of tradeoff studies , stakeholder requirements and system constraints (e.g. budget).
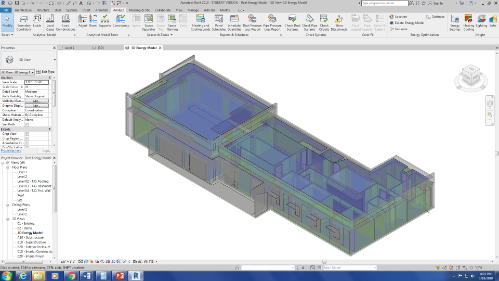
Building Energy Model in Autodesk Revit
Building Envelope
building envelope is the boundary boundary between the interior of the building and en environment. The building envelope is composed of walls, roof, door and windows. Roof and walls are mainly selected by their thermal insulation or R-Value. The higher the R-Value the better the thermal insulation of the material. Windows and doors are selected by it Solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC). The SHGC is the fraction of solar radiation through a window. The lower the SHGC of a window, the less solar heat it allows.
| Material | Technology | Rating |
|---|---|---|
| Roof |
Mechanically fastened thermoplastic polyolefin (TPO) roofing system 0/6in insulation on 5/8in frt. plywood decking The roof was coated with white paint to reduce the amount of solar radiation absorbed |
R-30 |
| Walls |
8” CM block wall with 3- part stucco with the following composition:
|
R-7.5 |
| Windows |
Window: Single Glazing Reflective tint |
SHGC 0.25 |
Lighting
The building lights are LED with dimming capabilities. Occupancy sensors and daylight sensors are part the lighting system. The occupancy sensors allow turning on the lights when someone is in the room and turn them after no detecting occupant s for a preset amount of time. Daylight sensors allow the control system to adjust the lights automatically to harvest daylight. Each room has manual control with programmable settings or light scenes.
HVAC
Heat Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) Systems are evaluated among other indicators by their Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) , Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) and tonnage.
The SEER is the ratio of cooling output divided by the consumed energy. A higher value of SEER is desirable. SEER is the maximum efficiency that the HVAC system can achieve under ideal conditions. HSPF is the heat output of the HVAC system divided by its energy usage. Higher values of HSPF are desirable. Tonnage is related to the work the HVAC has to do by removing heat from air. Tonnage of HVAC is selected to match the size of the space it needs to cool. More tonnage is associated with more cooling capacity and more energy consumption. For a given tonnage, SEER, HSPF, and cost can be used to select an HVAC system.
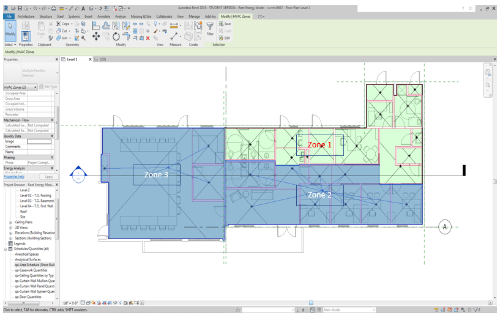
HVAC Zones
The HVAC technologies by zone are presented in the table below:
| Zone | HVAC Technology | Rating (SEER/HSPF/Ton) |
|---|---|---|
| Zone 1 | Split System (shared with zone 2) | 17/9.6/5.5 |
| Zone 2 | Split System (shared with zone 1) | 17/9.6/5.5 |
| Zone 3 | Split System (exclusive) | 17/9.6/5.5 |

 Give to Florida Tech
Give to Florida Tech 